Human Development Index is a tool developed by United Nations to track progress made by countries in improving the lives of the people. It is composite index which measures the average achievement of the countries in three basic parameters:
- Healthy and long life
- Access to knowledge
- Decent standard of living
Who publishes Human Development Index?
- Frequency of publication: Annually
- Published by: United Nations Development Program (UNDP)
- Report: Published in Human Development Report (HDR)
- First time published: In 1990
- Invented by: Pakistani Economist Mahbub ul Haq and Indian Nobel laureate Amartya Sen
Goalposts of HDI
The HDI sets minimum and maximum for each dimension which is referred as goal posts. The minimum and maximum value from each dimension is taken in order to translate the indicator to indices on scale of 0 or 1. Here
- 1 indicates high level of development
- 0 indicates very low level of development.
Goalposts of HDI
The HDI sets minimum and maximum for each dimension which is referred as goal posts. The minimum and maximum value from each dimension is taken in order to translate the indicator to indices on scale of 0 or 1. Here
- 1 indicates high level of development
- 0 indicates very low level of development.
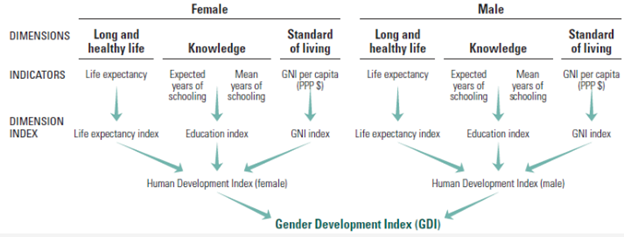
Human Development Index is the geometric mean of three indexes:
- Life Expectancy Index: The Health is determined by life expectancy at birth. The minimum value for life expectancy is 20 years and maximum is 80 years.
- Education Index: The Education Index is arithmetic mean of two indices:
- Expected years of schooling: The society can subsist without education but some level of education helps an individual to live quality life. The minimum for expected years schooling is set to 0 years and maximum is set to 18 years which is equivalent to achieving master’s degree in any country.
- Mean years of schooling: It is the mean years of schooling that an adult aged 25 has attained. The minimum value of this component is 0 years and maximum value is taken as 15 years.
- GNI Index: The decent standard of living is measured from Gross National Income (GNI) per capita adjusted to purchasing power parity (PPP) in US $. The goalpost taken for minimum income is US $100 and maximum is US $75000.

Categorisation of countries
The report places the countries in three categories of development:
- Low Human Development Countries: HDI between 0.0 and 0.5.
- Medium Human Development Countries: HDI between 0.5 and 0.8
- High Human Development Countries: HDI between 0.8 and 1.0.
Other indices in Human Development Report
- Inequality-adjusted Human Development Index (IHDI): One of the shortcomings of HDI was insensitivity of degree of inequality in each dimension. The IHDI can be views as real human development keeping accounting for inequality among people. The HDI is equal to IHDI provided there is no inequality across population.

- Gender Development Index (GDI): The GDI measures gender gaps in human development achievements by accounting for disparities between women and men in three basic dimensions of human development—health, knowledge and living standards using the same component indicators as in the HDI. The GDI is the ratio of the HDIs calculated separately for females and males using the same methodology as in the HDI. It is a direct measure of gender gap showing the female HDI as a percentage of the male HDI. It shows how much women are lagging behind their male counterparts and how much women need to catch up within each dimension of human development.
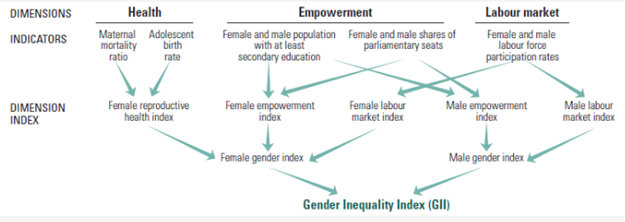
- Gender Inequality Index (GII): Girls and women have not gained gender equity yet. The females are discriminated against in health, education, political representation, labour market, etc.—with negative consequences for development of their capabilities and their freedom of choice. It measures the human development costs of gender inequality. Thus the higher the GII value the more disparities between females and males and the more loss to human development. The GII is an inequality index which measures gender inequalities in three important aspects of human development
- Reproductive health: It is measured by maternal mortality ratio and adolescent birth rates.
- Empowerment: It is measured by proportion of parliamentary seats occupied by females and proportion of adult females and males aged 25 years and older with at least some secondary education
- Economic status: It is expressed as labour market participation and measured by labour force participation rate of female and male populations aged 15 years and older.
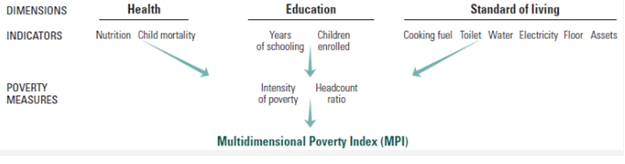
- Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI): Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI), published for the first time in the 2010 Report by UNDP and the Oxford Poverty & Human Development Initiative (OPHI). It measures the poverty by considering overlapping deprivations suffered by individuals at the same time. The index identifies deprivations across the same three dimensions as the HDI and shows the number of people who are multi-dimensionally poor. The dimension of MPI are:
- Health: It is measured by nutrition and child mortality rate.
- Education: It is measure by number of years of schooling and children enrollment rate.
- Standard of Living: It is measured by availability of Cooking fuel, toilet, water, electricity and assets.
We hope you liked this article on Human Development Index (HDI). Here are some useful articles for you to read next:
Download this article as PDF
Click to go to RBI Grade B Preparation Page