The Scheme of Mega Food Park aims at providing a mechanism to link agricultural production to the market by bringing together farmers, processors and retailers so as to ensure maximizing value addition, minimizing wastage, and increase in farmer’s income and creating employment opportunities particularly in rural sector. The Mega Food Park Scheme is based on “Cluster” approach and envisages creation of state of art support infrastructure in a well-defined agri / horticultural zone for setting up of modern food processing units in the industrial plots provided in the park with well-established supply chain. Mega food park typically consist of supply chain infrastructure including collection centers, primary processing centers, central processing centers, cold chain and around 25-30 fully developed plots for entrepreneurs to set up food processing units.
Objectives of Mega Food Park Scheme
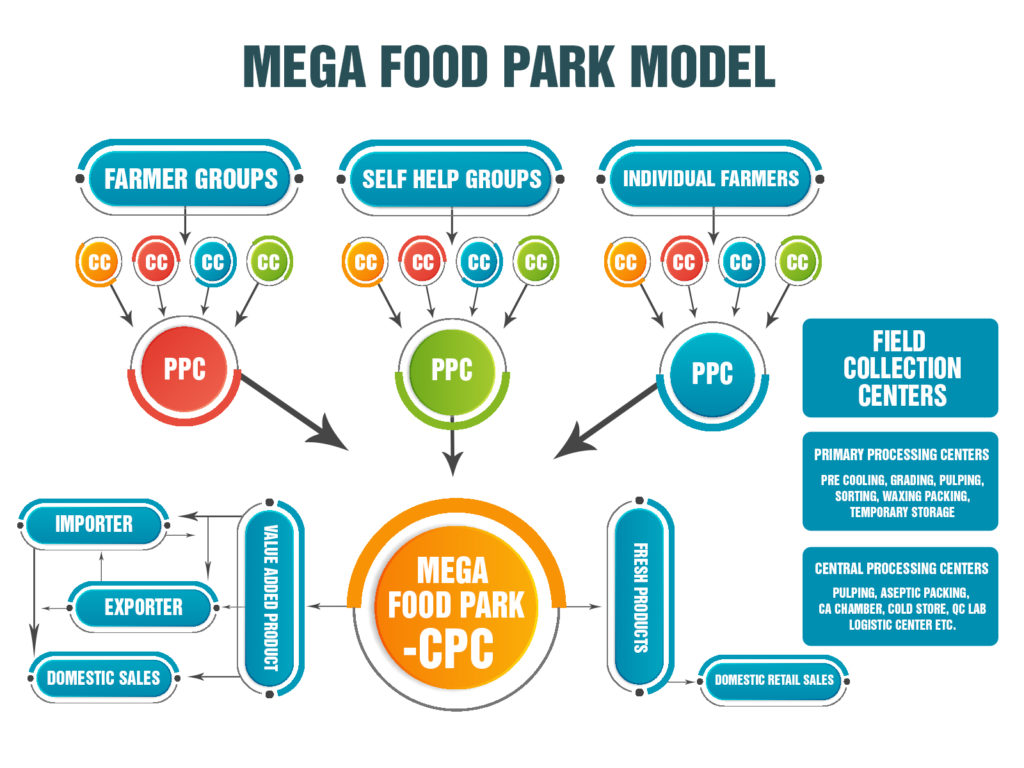
- To provide modern infrastructure facilities for the food processing along the value chain from the farm to the market with a cluster based approach based on a hub and spokes model.
- It includes creation of infrastructure for primary processing and storage near the farm in the form of Primary Processing Centres (PPCs) and Collection Centres (CCs) and common facilities and enabling infrastructure like roads, electricity, water, ETP facilities etc. at Central Processing Centre (CPC).
- Food Processing being capital incentive activity, common facilities are created at CPC to be used by the processing units on hire basis. This helps in reducing the cost of individual units significantly and makes them more viable.
Features of Mega Food Park Scheme
- The minimum land required for a Central Processing Centre in Mega Food Park is 50 acre and implementation period is 30 months.
- A cluster of 30-35 units is expected to come up in one Mega Food Park with an investment of about Rs. 250 Crore.
- It is likely to benefit about 6000 farmers/ producers directly and 25000-30000 farmers indirectly.
- The financial assistance under the scheme is provided in the form of grant-in-aid @ 50% of eligible project cost in general areas and @ 75% of eligible project cost in NE Region and difficult areas (Hilly States and ITDP areas) subject to maximum of Rs. 50 crore per project.
Special Purpose Vehicle
The Mega Food Park project is implemented by a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) which is a Body Corporate registered under the Companies Act. State Government, State Government entities and Cooperatives are not required to form a separate SPV for implementation of Mega Food Park project. Subject to fulfillment of the conditions of the Scheme Guidelines, the funds are released to the SPVs. The Scheme is under the purview of the Ministry of Food Processing Industries
Progress of Mega Food Park Scheme
So far following 18 Mega Food Parks are operational:
- Srini Mega Food Park, Chittoor, Andhra Pradesh.
- Godavari Mega Aqua Park, West Godavari, Andhra Pradesh.
- North East Mega Food Park, Nalbari, Assam.
- Gujarat Agro Mega Food Park, Surat, Gujarat.
- Cremica mega Food park, Una, Himachal Pradesh.
- Integrated Mega Food Park, Tumkur, Karnataka.
- Indus Mega Food Park, Khargoan, Madhya Pradesh.
- Paithan Mega Food Park, Aurangabad, Maharashtra.
- Satara Mega Food Park, Satara, Maharashtra.
- MITS Mega Food Park, Rayagada, Odisha.
- International Mega Food Park, Fazilka, Punjab.
- Greentech Mega Food park, Ajmer, rajasthan.
- Patanjali Food and Herbal Park, Haridwar, Uttarakhand.
- Himalayan Mega Food Park, Udham Singh Nagar, Uttarakhand.
- Jangipur Bengal Mega Food Park, Murshidabad, West Bengal.
- Tripura Mega Food Park, West Tripura, Tripura.
- Smart Agro Mega Food Park, Nizamabad, Telangana.
- Avantee Mega Food Park, Dewas, Madhya Pradesh.
We hope you liked this article on Mega Food Park Scheme. Here are some useful government schemes for you to read next:
Download this article as PDF
Click to go to RBI Grade B Preparation Page | Click to read more government schemes