Data Communication refers to the transmission of data between two devices via some transmission medium such as optical wires. The data can be in form of text, numbers, images, audio, video etc. The efficiency of data communication depends upon four fundamental characteristics: delivery, accuracy, timeliness and jitter.
Components of Data Communication
A data communication system has five components:
- Message: It is the actual information that is communicated. Format of information can be form of text, numbers, images, audio, and video.
- Sender: It is a device that sends message. The sender can be computer, mobile phone, workstation etc.
- Receiver: It is the device which receives message. It can be computer, mobile phone, workstation etc.
- Transmission Medium: It is the physical path through which message travels from sender to receiver. It can be twisted-pair wire, coaxial cable, radio waves etc.
- Protocol: It is the set of rules that controls data communication. It represents an agreement between the communicating devices. Without a protocol, two devices may be connected but not communicating.
Modes of data flow in data communication
The data transmission between two devices can take place in three ways:
- Simplex Mode
- Half-Duplex Mode
- Full-Duplex Mode
Lets’ understand these modes.
Simplex Mode
The communication in this mode is one-way i.e. unidirectional. One out of two devices will be sender and other one will be receiver.

The sender can only send the data and receiver can only receive the data. The sender cannot receive the data and receiver cannot send the data. It is like one-way street. The example of simplex mode is computer-printer communication.
Half-Duplex Mode
In half-duplex mode, each device can send and receive the data. The data can flow in both the direction but only in one direction at a time. The transmission can occur only in one direction at a time. It is like one-lane road with traffic allowed in both directions.
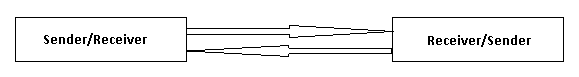
The example of half-duplex mode is walky-talky, internet browsing etc.
Full-Duplex Mode
In full-duplex mode, the data can be transmitted and received simultaneously. The data can flow in both directions at the same time. It is like two-way street with traffic flowing in both the directions.

It is the fastest mode of communication. The example of full-duplex mode is telephonic conversation; both the people on telephone line can talk and listen.
Download PDF
Read next: Network Topologies ››
« Back to Course page